共计 3645 个字符,预计需要花费 10 分钟才能阅读完成。
1、this
1.1、this 概述
this 是自身的一个对象,代表对象本身,是非静态对象,可以理解为:指向对象本身的一个指针。
public class ThisDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//this.print();//this 是非静态对象
new ThisDemo().view();
}
public void view() {this.print();}
public void print() {System.out.println("ThisDemo");
}
}
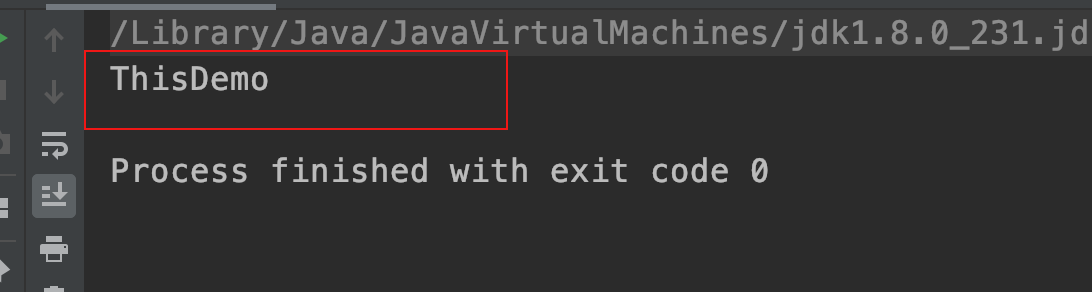
运行结果:
1.2、this 应用
1.2.1、直接引用
this 相当于是指向当前对象本身。
public class ThisDemo01 {String s = "Hello";
public ThisDemo01(String s1) {System.out.println("s =" + s1);
//this 当前对象,调用 s 属性
System.out.println("1 -> this.s =" + this.s);
this.s = s1;// 把参数值赋给成员变量,成员变量的值改变
System.out.println("2 -> this.s =" + this.s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {ThisDemo01 x = new ThisDemo01("HelloWorld!");
System.out.println("s=" + x.s);// 验证成员变量值的改变
}
}
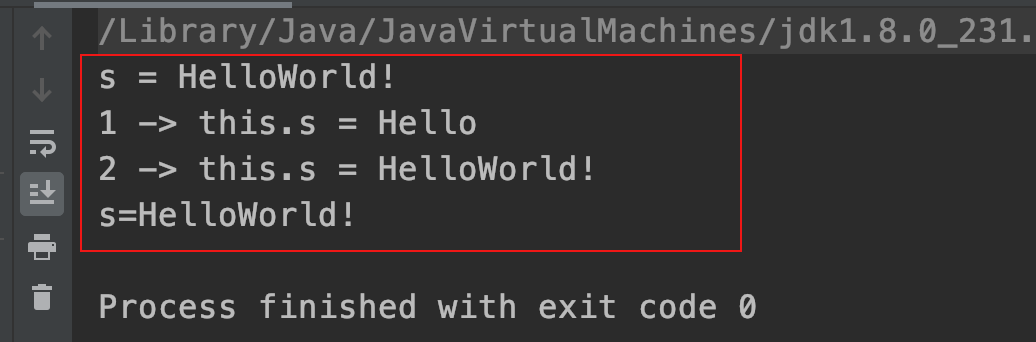
运行结果:
1.2.2、形参与成员变量名字重名,用 this 来区分
class Person {private int age = 10;
public Person() {System.out.println("初始化年龄:" + age);
}
public int GetAge(int age) {this.age = age;
return this.age;
}
}
public class ThisDemo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Person Harry = new Person();
System.out.println("Harry's age is " + Harry.GetAge(12));
}
}
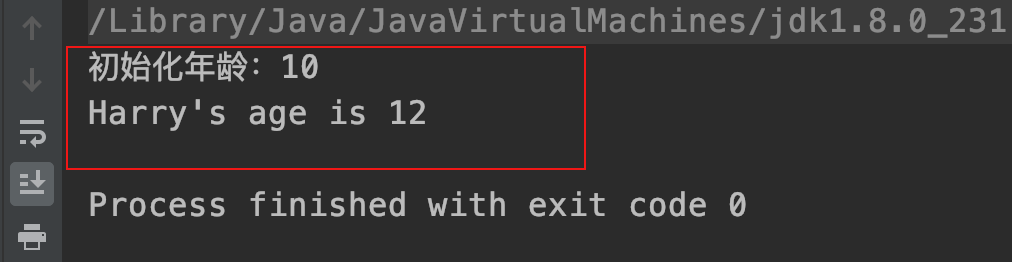
运行结果:
1.2.3、引用构造函数
这个我们用 super 一起讲。
1.2.4、同时传递多个参数
public class ThisDemo03 {int x;
int y;
static void showtest(ThisDemo03 tc) {// 实例化对象
System.out.println(tc.x + " " + tc.y);
}
void seeit() {showtest(this);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {ThisDemo03 p = new ThisDemo03();
p.x = 9;
p.y = 10;
p.seeit();}
}
运行结果:
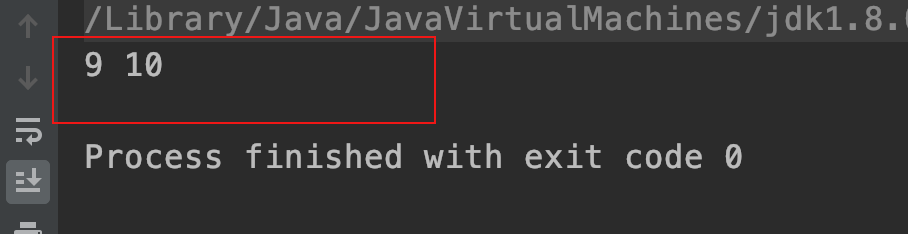
2、super
2.1、super 概述
super 可以理解为是指向自己超(父)类对象的一个指针,而这个超类指的是离自己最近的一个父类。
2.2、super 应用
2.2.1、直接引用
与 this 类似,super 相当于是指向当前对象的父类,这样就可以用 super.xxx 来引用父类的成员。
class A{public void print(){System.out.println("A");
}
}
public class SuperDemo01 extends A{public static void main(String[] args) {//super.print();//super 是非静态对象
new SuperDemo01().view();
}
public void view(){super.print();}
}
运行结果:
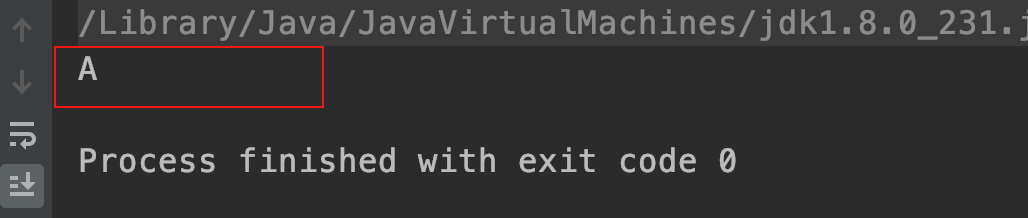
2.2.2、子类成员重写父类成员后
子类中的成员变量或方法与父类中的成员变量或方法同名
class Country {
String name;
void value() {name = "China";
}
}
public class City extends Country {
String name;
void value() {name = "Shanghai";
super.value(); // 调用父类的方法
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {City c=new City();
c.value();}
}
运行结果:
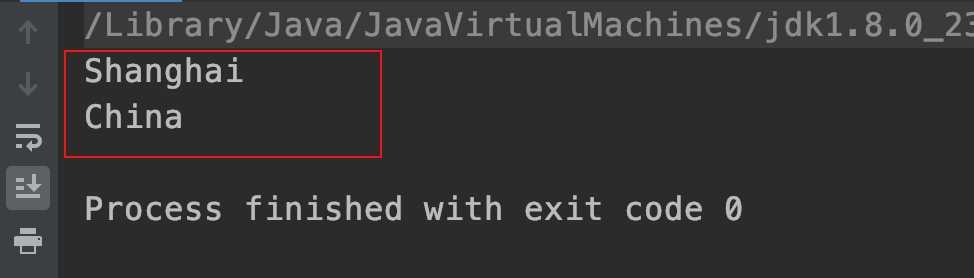
2.2.3、引用构造函数
super(参数):调用父类中的某一个构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句)。
this(参数):调用本类中另一种形式的构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句)。
package cn.com.tyschool.demo001;
class Persones{public void prt(String s) {System.out.println(s);
}
// 构造方法 (1)
public Persones() {prt("父类·无参数构造方法:"+"A Person.");
}
// 构造方法 (2)
public Persones(String name) {prt("父类·含一个参数的构造方法:"+"A person's name is " + name);
}
}
public class Chinese extends Persones {Chinese() {super(); // 调用父类构造方法(1)
prt("子类·调用父类”无参数构造方法“:"+"A chinese coder.");
}
Chinese(String name) {super(name);// 调用父类具有相同形参的构造方法(2)
prt("子类·调用父类”含一个参数的构造方法“:"+"his name is" + name);
}
Chinese(String name, int age) {this(name);// 调用具有相同形参的构造方法(3)
prt("子类:调用子类具有相同形参的构造方法:his age is" + age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {Chinese cn = new Chinese();
cn = new Chinese("codersai");
cn = new Chinese("codersai", 18);
}
}
运行结果:
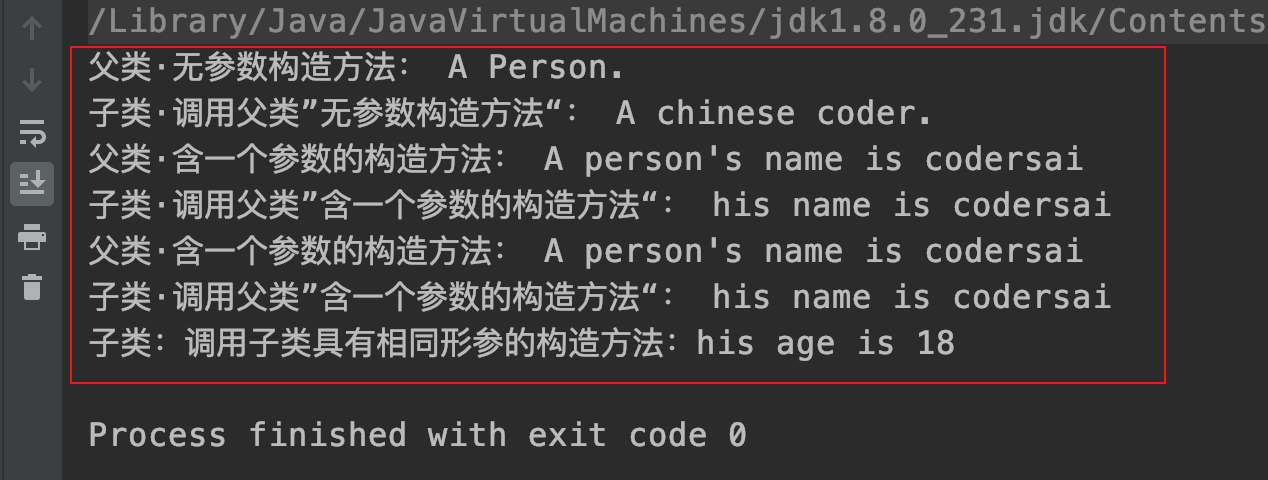
3、this/super 区别
3.1、super()/this()
super(参数):调用父类中的某一个构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句)
this(参数):调用本类中另一种形成的构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句)
class A{public A(){System.out.println("无参");
}
public A(int x){System.out.println("参数为:"+x);
}
}
class B extends A{public B(){//super();
super(12);
}
public static void main(String args[]){new B();}
}
class B{public B(){this(12);
}
public B(int x){System.out.println("参数为:"+x);
}
public static void main(String args[]){new B();}
}
3.2、super/this
super: 它引用当前对象的直接父类中的成员(用来访问直接父类中被隐藏的父类中成员数据或函数),基类与派生类中有相同成员定义时如:
super. 成员(成员变量、成员方法)
this:它代表当前对象名(在程序中易产生不同意义,应使用 this 来指明当前对象;如果函数的形参与类中的成员数据同名,这时需用 this 来指明成员变量名)
class A{public void a(){System.out.println("a");
}
}
class B extends A{public static void main(String args[]){B b=new B();
b.b();}
public void a(){System.out.println("b");
}
public void b(){super.a();}
}
class B{int x=12;
public static void main(String args[]){new B().b(13);
}
public void b(int x){System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(this.x);
}
}
3.3、super/this 为非静态成员
class B{public static void main(String args[]){//super. 成员 // 不能在静态方法里面使用
}
}
class B{public static void main(String args[]){//this. 成员 // 不能在静态方法里面使用
}
}
正文完
星哥玩云-微信公众号